Tinea or dermatophytes, is a common fungal infection which develops on the outermost layer of the skin. It can be distinguished by a ring-shaped, scaly rash or patches which are red around the edges and clearer to the center. It can be very itchy. The name does not refer to worms itself, but rather to the circular appearance of the fungal lesions (1).
What is the Cause of Dermatophytes?
The fungus, known as dermatophyte, is the cause of the irritation on the skin’s surface. This fungi lives off of the dead tissue on the skin, hair, or nails. It grows in areas which are moist and warm. These areas could be in skin folds, such as the groin or between the toes (2).
It is contagious and can be spread by contact with humans and animals. In rare cases, it can be contracted from soil or objects that have been infected or come in contact with the fungus. The risk increases if you (3):
- Sweat excessively
- Have minor lesions on the skin
- Share objects like clothing that has the fungus on it
- Do sports that involve a lot of contact, such as wrestling
- Use public showers or locker rooms
- Live in areas with a warm climate
- In close contact with animals
- Swim in public pools
- Use tanning beds
Take Home Note:
This fungus lives off of dead tissue on the skin, hair, or nails. The fungus is contagious and is caused by contact with other humans, animals, and objects that are infected. Areas of the body which are warm and moist are usually good places where the fungus thrives.
Signs and Symptoms
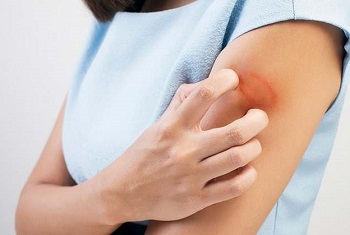 The most common way of detecting ringworm is by seeing a red, scaly patch or bump on the surface of the skin. As it develops, the edges of the patch become redder and are raised or feel bumpy. The center of the patch is usually whiter and it is scaly or marked with a scattering of red bumps (4).
The most common way of detecting ringworm is by seeing a red, scaly patch or bump on the surface of the skin. As it develops, the edges of the patch become redder and are raised or feel bumpy. The center of the patch is usually whiter and it is scaly or marked with a scattering of red bumps (4).
Take Home Note:
It is commonly recognized by the red, circular-shaped patch on the surface of the skin. The edges of this patch are very red and characterized by a bumpy raised surface. The center of the patch is usually whiter and scaly or marked with red bumps.
Classification
The type of ringworm depends on the location on the body. These include (5):
- Athlete’s foot (Tinea pedis)
- Jock itch (Tinea cruris)
- Scalp (Tinea capitis)
- Nail (Tinea unguium)
- Body (Tinea corporis)
Take Home Note:
It is classified by the area on the body where it is located. It may look different on certain areas due to the location, however the signs and symptoms will be the same.
What Antifungal Treatments are Available?
Treatment depends on where the infection is located on the body and how severe it is. In most cases, a healthcare professional will recommend the use of a drug which can be purchased over-the-counter. Other types would require a prescription medication (6).
 If it is located on the skin, like athlete’s foot and jock itch, then a topical treatment can be used. This is in the form of a non-prescription antifungal lotion, cream, or powder. The total duration of treatment should be around 2 weeks; 1 week to stop the symptoms and a further 7 days to prevent recurrence. If the infection does not disappear with this form of treatment, it is recommended that you see your healthcare professional (7).
If it is located on the skin, like athlete’s foot and jock itch, then a topical treatment can be used. This is in the form of a non-prescription antifungal lotion, cream, or powder. The total duration of treatment should be around 2 weeks; 1 week to stop the symptoms and a further 7 days to prevent recurrence. If the infection does not disappear with this form of treatment, it is recommended that you see your healthcare professional (7).
If it is located on the scalp, then you will need to treat it with a prescription antifungal medication. This is because the fungal infection is found at the root of the hair follicles on the scalp and topical treatments do not penetrate so deeply. Systemic treatment is required as this medication is administered orally and it spreads throughout the entire body. It is recommended that oral treatment be taken for 1 to 3 months (8).
Take Home Note:
Different treatments are prescribed for different types of infection, and usually the location thereof. If it is located on the feet or groin (basically the skin), then a topical treatment will be given. These include creams, lotions, and powders. If it is located on the scalp, then a systemic treatment will be prescribed. This will be orally administered to ensure the treatment reaches the entire body. If symptoms do not disappear, it is recommended to see your healthcare professional.
Prevention
It is quite difficult to prevent getting infected as it is so easy to come into contact with a person, animal, or area that has been infected. This is because the fungus is common and contagious even before there are any traces of symptoms. You can reduce the risk of getting infected by following these steps (9,10):
 Be educated – Know the symptoms and causes to avoid contact with people, animals, or objects that may be infected.
Be educated – Know the symptoms and causes to avoid contact with people, animals, or objects that may be infected.- Personal hygiene – Wash regularly if you sweat a lot or live in an area with a warm climate. Wash your hands often to prevent spreading of infection. Avoid wearing thick clothing for long periods of time, especially in warm areas. Wash clothes, towels, and bedding as often as possible. Wear appropriate footwear in locker rooms and public showers. Change your underwear and clothes at least once a day. Keep fingernails short and clean. Shower immediately after any form of contact sports and also wash any clothing or equipment used during this time.
- Prevent contact with infected animals – Keep your pets clean by giving them a bath and washing their bedding often. If your pet has a patch of hair missing with the characteristics of a red patch, see your veterinarian.
- Respect personal items – Do not use other people’s clothes, hairbrush, towel, bedding, or other personal items. Also do not share these items with others.
Take Home Note:
It is quite common to be infected by this fungus. However, there are ways to reduce the risk of becoming infected. It is important to know the signs and symptoms and to educate others as well. Personal hygiene is a must, especially if you are living in a warm area where you sweat a lot. Animals with bald patches on their coats may be infected. Also keep your personal items to yourself and do not use other peoples’ personal items.
Ultimate Take Home Message
Tinea is a common contagious fungus which can be contracted by coming into contact with other humans, animals, or objects which are infected. It is characterized by a red circular-shaped patch on the surface of the skin. The edges are bumpy. There are different types, and each type is classified and treated according to the location. Treatment can be topical, by using creams, lotions, or powders. If it is found on the scalp, then a prescription medication must be used. These are systemic and must be taken orally. There are ways to reduce the risk of becoming infected. The most important method is to stay clean and prevent contact with those who are infected.



